(high) impact polystyrene (IPS or HIPS)
Back to Information about polystyrene
1 General description
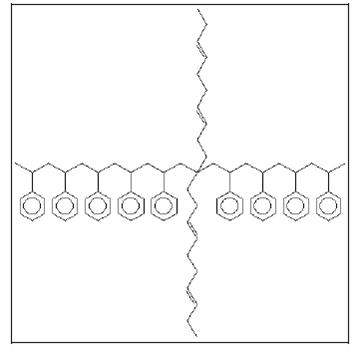
The mechanical properties of the relatively brittle PS moulding materials can be considerably improved by adding rubbers, i.e. polybutadiene. High impact polystyrene is also known as toughened PS or rubber-modified PS; ISO 2897-2 defines it as impact resistant polystyrene (IPS). Early production processes for HIPS were based on mixing PS moulding materials with a rubber component. Polymerisation of styrene in the presence of polybutadiene is, however, much more effective. A two-phase system is formed due to the immiscibility of polystyrene and polybutadiene. Polystyrene forms the continuous phase (matrix) and polybutadiene does the disperse phase (rubber particle). The rubber particles contain small inclusions of polystyrene. The rubber particles in HIPS generally have a diameter of 0.5 – 10 Wm. They, therefore, scatter visible light and the transparency of the PS moulding materials is lost. Figure 4.2 shows the structure of HIPS containing the polystyrene and polybutadiene chains. The additives commonly used with moulding PS grades can also be compounded into HIPS. In addition, antioxidants are used for rubber stabilisation and flame-retardants are added for special PS applications.
Figure 1: Molecular structure of high impact polystyrene
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) has many uses and applications because of its ease of processing, low cost and high performance. It is converted to products by injection moulding, extrusion and thermoforming. Major end uses include packaging, disposable containers and cups, consumer electronics, razors, audio and video cassettes, TV cabinets, refrigeration liners, computer housings, and toys. HIPS is also used to make engineering resin blends with polyphenylene oxide for the automotive industry.
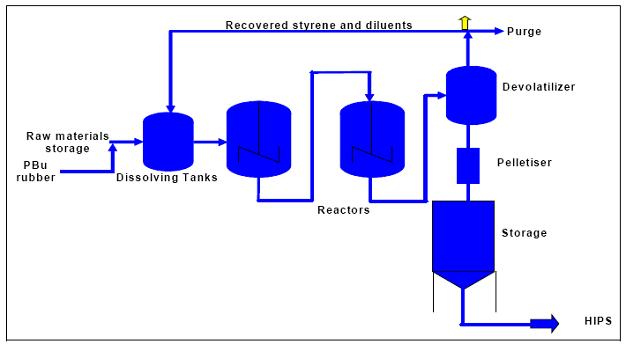
2 Flow diagram of HIPS production
Figure 2: Flow diagram showing HIPS production
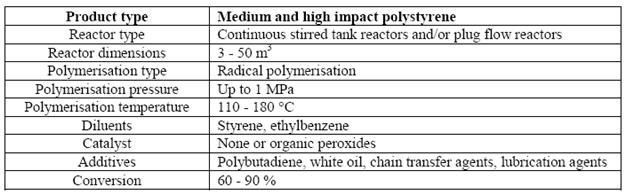
3 Technical parameters
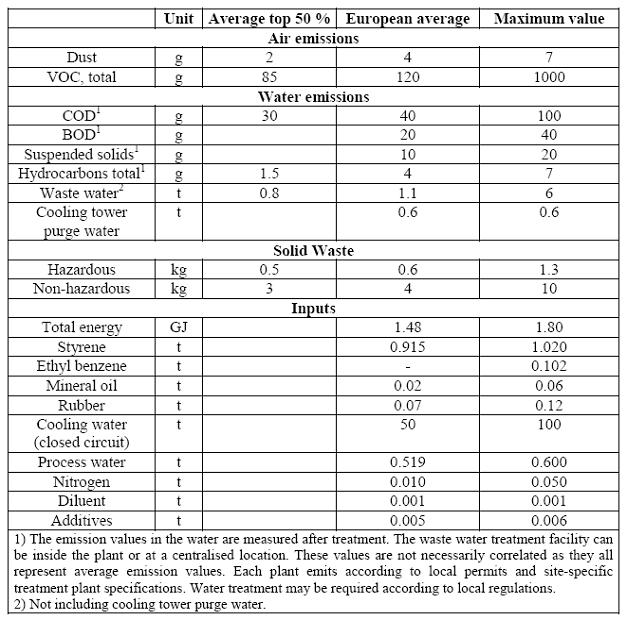
4 Emission and consumption data of HIPS plants
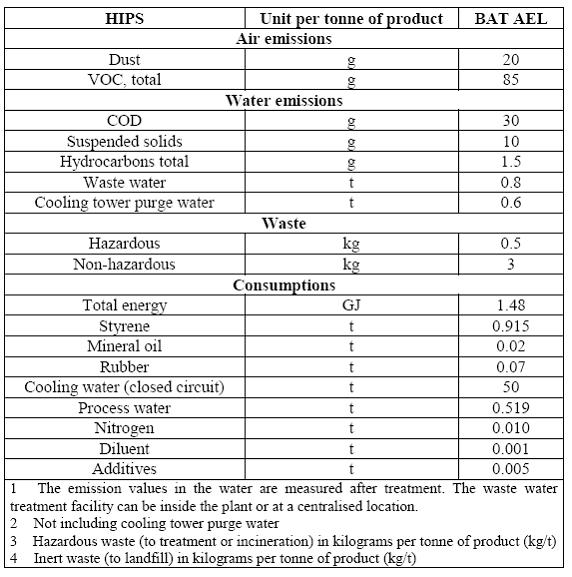
5 Emission and consumption levels associated with BAT for the production of polystyrene
Literature: BAT for Polymers, October 2006
Back to Information about polystyrene