Difference between revisions of "Cooling processes"
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| − | [[Image:cooling processes in general!. | + | [[Image:cooling processes in general!.JPG]] |
;help topics | ;help topics | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 13 October 2010
Back to EFFICIENCY FINDER
1. OBJECTIVE
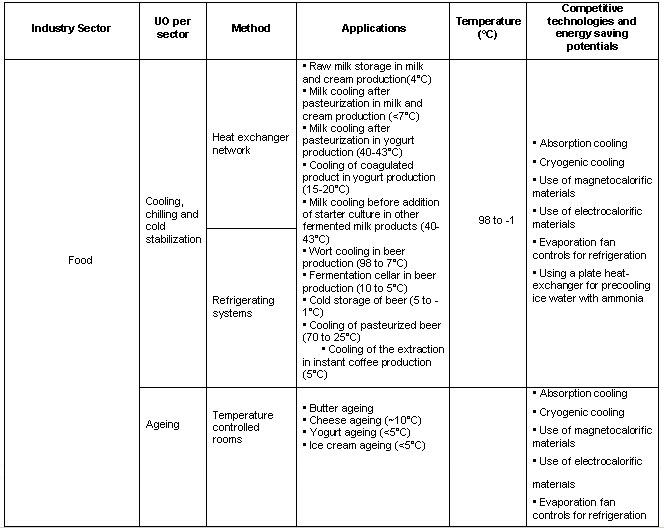
The objective of cooling processes in the food industry is to reduce or maintain the temperature of a product in a lower level for a period of time.
Cooling, chilling, cold stabilization and ageing are the typical processes included in this category.
2. FIELD OF APPLICATION
Cooling is a process which is carried out in a wide range of industries, including foodstuffs, galvanizing and many others.
3. DESCRIPTION OF TECHNIQUES, METHODS AND EQUIPMENT
In cooling systems, cooling is carried out by passing the product through a heat exchanger or cooler or cooling the vessels. A cooling medium is always used to achieve the temperature reduction and often the cooling medium is recirculated in the cooling system. The equipment used for freezing can also be used for cooling (BAT in the Food, Drink and Milk Industries, June 2005).
- help topics
- magnetocaloric
- absorption
- absorption cooling
- electrocaloric
- evaporation
- refigeration
- cryogenic
- ammonia
4. RELEVANT PARAMETERS TO ENERGY
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Medium
- Material characteristics (e.g. temperature sensitivity)
Back to EFFICIENCY FINDER