Difference between revisions of "Information about clothes"
(→Measures to reduce energy consumption) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
In laundries, energy is necessary to generate process heat (steam, hot water). Energy sources are gas, electricity and fuel oil (extra light) and fuel oil (heavy: S). | In laundries, energy is necessary to generate process heat (steam, hot water). Energy sources are gas, electricity and fuel oil (extra light) and fuel oil (heavy: S). | ||
gas and electricity are used for | gas and electricity are used for | ||
| − | * | + | * direct machine heating as well as for |
| − | * | + | * indirect application to heat transfer media |
Heavy fuel oil is normally applied in industrial plants only due to complex legal requirements for its application | Heavy fuel oil is normally applied in industrial plants only due to complex legal requirements for its application | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Steam characteristics | Steam characteristics | ||
| − | + | * high heat capacity | |
| − | + | * excellent transfer capacity | |
| − | + | * constant efficiency at max. power | |
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
Steam characteristics | Steam characteristics | ||
| − | + | * high heat capacity | |
| − | + | * excellent transfer capacity | |
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Local supply (heating) | Local supply (heating) | ||
| − | * | + | * Individual heating of each machine |
| − | * | + | * for laundries at a capacity of up to 500 kg textiles/day |
| − | * | + | * Gas or electricity (prerequisite: local favourable fees) |
| − | * | + | * Advantage of individual heating: flexible usage of resources dependent on amount of textiles |
| − | * | + | * Economical: no higher use of energy than required |
| − | * | + | * Efficient and environmentally friendly |
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
Central supply | Central supply | ||
| − | * | + | * for laundries at a capacity of more than 500 kg laundry |
| − | * | + | * most important medium is steam, sometimes hot water or thermal oil |
| − | * | + | * Advantage: distribution of heating medium constantly possible as well as the possibility of direct heating of the washing liquor |
| − | * | + | * Performance of steam generator is very important |
| − | * | + | * At high utilization, all machines may require heating energy at same time -> boiler should be capable to supply all machines with enough steam,even at high production peaks |
Revision as of 13:54, 18 April 2017
Contents
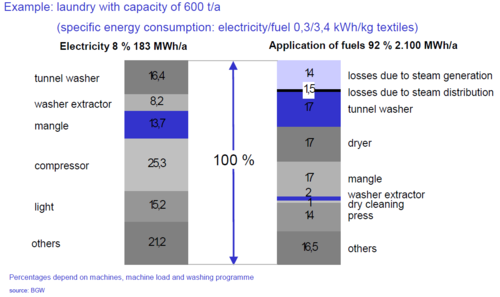
Usage of energy in laundries
In laundries, energy is necessary to generate process heat (steam, hot water). Energy sources are gas, electricity and fuel oil (extra light) and fuel oil (heavy: S). gas and electricity are used for
- direct machine heating as well as for
- indirect application to heat transfer media
Heavy fuel oil is normally applied in industrial plants only due to complex legal requirements for its application
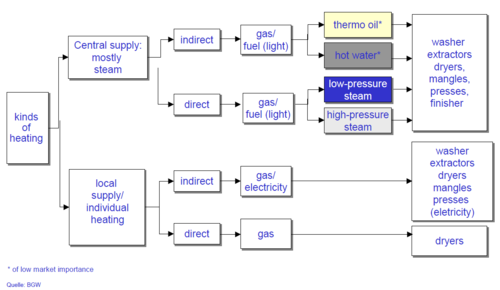
Distribution of energy in laundries
Energy sources in laundries
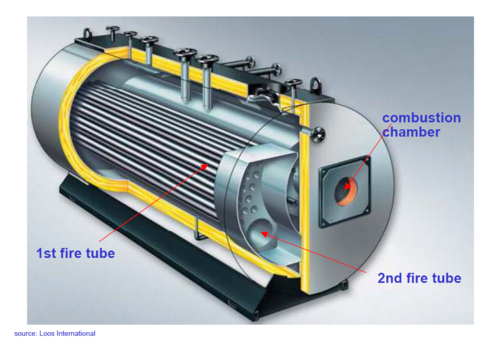
High pressure steam:
Steam pressure > 1,0 bar, usually: 8 -12 bar (above atmospheric pressure), temperatures: 175 - 191 °C
Steam characteristics
- high heat capacity
- excellent transfer capacity
- constant efficiency at max. power
Application technology
+ direct steam flow (washing and steam process, therefore short heating up of heating washing liquor)
+ high efficiency (economic)
+ reserve at high peaks of consumption (big boiler)
- high acquisition costs
- inspection by legislation required
Low pressure steam:
Steam pressure 0,5 - 1,0 bar, usually: 0,5 bar (above atmospheric pressure), temperatures: max. 120 °C
Steam characteristics
- high heat capacity
- excellent transfer capacity
Application technology
+ short heating up intervals
+ simple handling and maintenance
+ low acquisition costs
+ no legal requirement of inspection (TÜV),registration of boiler only
- temperature max. 120 ºC, therefore inapplicable for mangles, tumblers, presses etc.
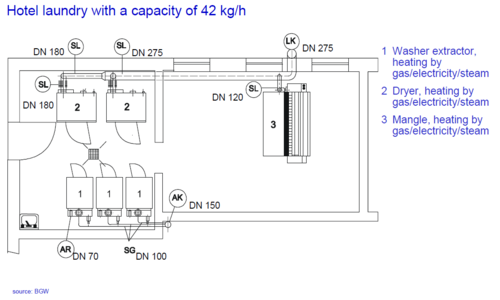
Heat supply in small laundries
Local supply (heating)
- Individual heating of each machine
- for laundries at a capacity of up to 500 kg textiles/day
- Gas or electricity (prerequisite: local favourable fees)
- Advantage of individual heating: flexible usage of resources dependent on amount of textiles
- Economical: no higher use of energy than required
- Efficient and environmentally friendly
Heat supply in industrial laundries
Central supply
- for laundries at a capacity of more than 500 kg laundry
- most important medium is steam, sometimes hot water or thermal oil
- Advantage: distribution of heating medium constantly possible as well as the possibility of direct heating of the washing liquor
- Performance of steam generator is very important
- At high utilization, all machines may require heating energy at same time -> boiler should be capable to supply all machines with enough steam,even at high production peaks
Measures to reduce energy consumption
Active environmental protection:
Optimize energy consumption by
- Burner optimization
- Use of adapted burners
- Reduced washing temperatures
- Optimized washing mechanics (without negative influence on washing performance as well as life cycle of textiles!)
Passive environmental protection:
Reduce energy consumption by
- Technical measures to reduce energy consumption
- Application of heat exchangers to reduce temperature of effluent water