Difference between revisions of "Plating cadmium in metal industry"
From Efficiency Finder
m (Protected "Plating cadmium in metal industry" [edit=autoconfirmed:move=autoconfirmed]) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
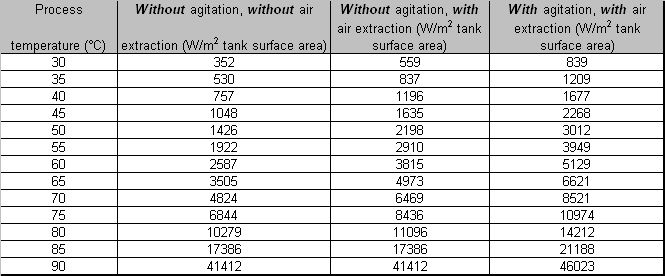
| + | *;Energy losses from the surface area of heated process solutions | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Energy losses from the surface area of heated process solutions.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | LITERATURE: BAT for the Surface Treatment of Metals and Plastics, May 2005 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Back to [[Subsection DJ metals|EFFICIENCY FINDER FOR METAL INDUSTRY]] | Back to [[Subsection DJ metals|EFFICIENCY FINDER FOR METAL INDUSTRY]] | ||
Revision as of 11:21, 1 December 2010
Back to EFFICIENCY FINDER FOR METAL INDUSTRY
- Typical parameters of the process
| Process | Temperature [°C] | Heat transfer medium | Residence time | Chemicals | Concentration | Details | Literature |
| Plating with cadium cyanide solutions | 20-35 | NaOh, NaCN, cadmium | NaOh: 20 g/l; NaCN: 120 g/l; cadmium: 20-30 g/l | BAT for the surface treatment of metals and plastics, August 2006 | |||
| Plating with cadmium fluoroborated solutions | 20-35 | Cadmium fluoroborate, ammonium fluoroborate, boric acid | Cadmium fluoroborate: 250 g/l; ammonium fluoroborate: 60 g/l; boric acids: 25 g/l | ||||
| Plating with cadium sulphate solutions | 18-30 | Cadmium sulphate, sulphuric acid | Cadmium sulphate: 52-85 g/l; sulphuric acid: 50-120 g/l | ||||
| Plating with cadium chloride solutions | Cadmium chloride, ammonium chloride, complexing agent (EDTA, NTA) | Cadmium chloride: 114 g/l; ammonium chloride: 112 g/l; complexing agent (EDTA,NTA): 180 g/l |
- Energy losses from the surface area of heated process solutions
LITERATURE: BAT for the Surface Treatment of Metals and Plastics, May 2005