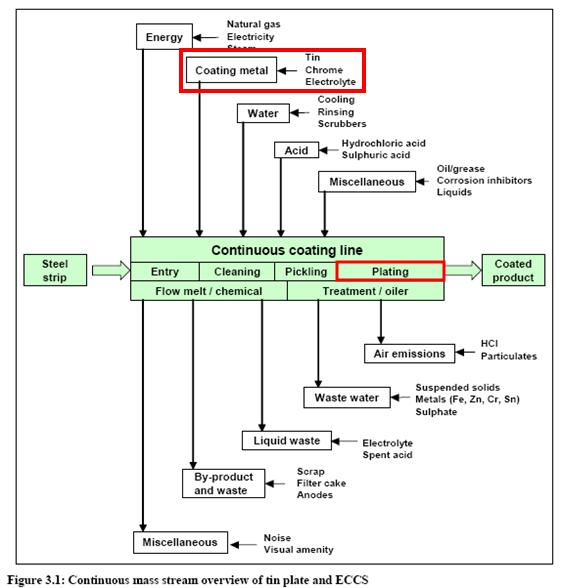
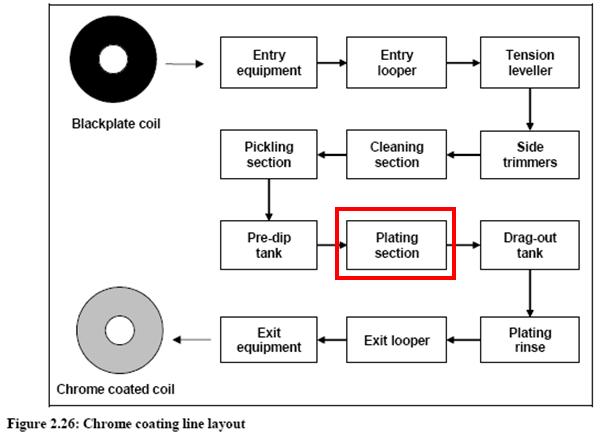
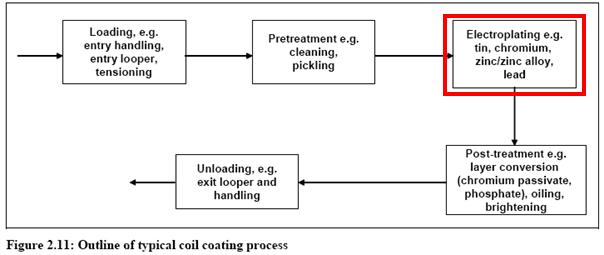
Plating chromium in metal industry
From Efficiency Finder
Back to EFFICIENCY FINDER FOR METAL INDUSTRY
- Plating chromium flowsheet
Literature: BAT for the Surface Treatment of Metals and Plastics, 2006
- Typical parameters of the process
| Process | Temperature [°C] | Heat transfer medium | Residence time | Chemicals | Concentration | Details | Literature |
| Bright hexavalent chromium plating | Chromic acids, sulpahtes as the primary catalyst such as fluoride ions | Chromic acids: 80-400 g/l; sulphate: 0,8-5 g/l; fluoride ions: <2% of the concentartion of the chromic acid | BAT for the surface treatment of metals and plastics, August 2006 | ||||
| Bright chromium plating (decoration) | 20-45 | 2-13 min | Trivalent chromium | 20 g/l | |||
| Bright trivalent chromium electroplating | |||||||
| Black chromium plating | Hexavalent chromium acid; catalysts (nitrates, fluorides) | Hexavalent chromium acid electrolytes: 350-520 g/l | |||||
| Hard chromium plating | Chromium acid and one the following catalysts: sulpahte ions, mixed sulpahte and fluoride ions, pre-prepared proprietary fluoride- free | Chromic acid: 180-350 g/l; sulpahte ions: 1,8-6 g/l; mixed sulphate and fluoride ions: <2% of the content of the chromic acid; pre-prepared proprietary fluoride-free: <2% of the content of the chromic acid |
- Energy losses from the surface area of heated process solutions
Image:Energy losses from the surface area of heated process solutions.jpg
LITERATURE: BAT for the Surface Treatment of Metals and Plastics, May 2005