Difference between revisions of "Soapstock"
(Created page with "Back to EFFICENCY FINDER OF FOOD INDUSTRY <br> Back to Biobased products in fats/oils") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Back to [[Biobased products in fats/oils]] | Back to [[Biobased products in fats/oils]] | ||
| + | === Description === | ||
| + | As mentioned above, crude edible oils contain different types of undesirable substances. The quantity of free fatty acids (ffa) is about 0.5 to 0.7%. The removal of ffa (< 0.1% in refined oil) can be achieved either by caustic neutralisation in a chemical refinery or by distillation in a physical refinery. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The chemical neutralisation consist of an addition of caustic soda (at 75-110ºC) to saponify the ffa in order to precipitate soaps in the heavy aqueous phase and remove the heavy phase, called soapstock, by using gravity or centrifugation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Block diagram of the physical and chemical refining ===== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:Refining.jpg]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Source: Edible Oil Processing,R.S.; The ACVS Lipid Library | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Valorisation techniques === | ||
| + | Soapstock always requires subsequent treatment. The method of treating soapstock is known as splitting. The soapstock is split into fatty acids (acid oil) and wash water by acidification with sulphuric acid. | ||
| + | The soapstock can be sold to a third party and in case of an integrated plant, there is an option to recycle it into the process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === References === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Back to [[Biobased products in fats/oils]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Back to [[Subsection DA food|EFFICENCY FINDER OF FOOD INDUSTRY]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:33, 21 November 2014
Back to EFFICENCY FINDER OF FOOD INDUSTRY
Back to Biobased products in fats/oils
Contents
Description
As mentioned above, crude edible oils contain different types of undesirable substances. The quantity of free fatty acids (ffa) is about 0.5 to 0.7%. The removal of ffa (< 0.1% in refined oil) can be achieved either by caustic neutralisation in a chemical refinery or by distillation in a physical refinery.
The chemical neutralisation consist of an addition of caustic soda (at 75-110ºC) to saponify the ffa in order to precipitate soaps in the heavy aqueous phase and remove the heavy phase, called soapstock, by using gravity or centrifugation.
Block diagram of the physical and chemical refining
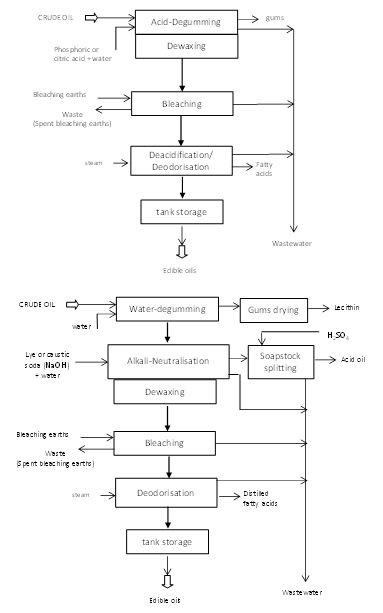
Source: Edible Oil Processing,R.S.; The ACVS Lipid Library
Valorisation techniques
Soapstock always requires subsequent treatment. The method of treating soapstock is known as splitting. The soapstock is split into fatty acids (acid oil) and wash water by acidification with sulphuric acid. The soapstock can be sold to a third party and in case of an integrated plant, there is an option to recycle it into the process.
References
Back to Biobased products in fats/oils
Back to EFFICENCY FINDER OF FOOD INDUSTRY